
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug Regimen
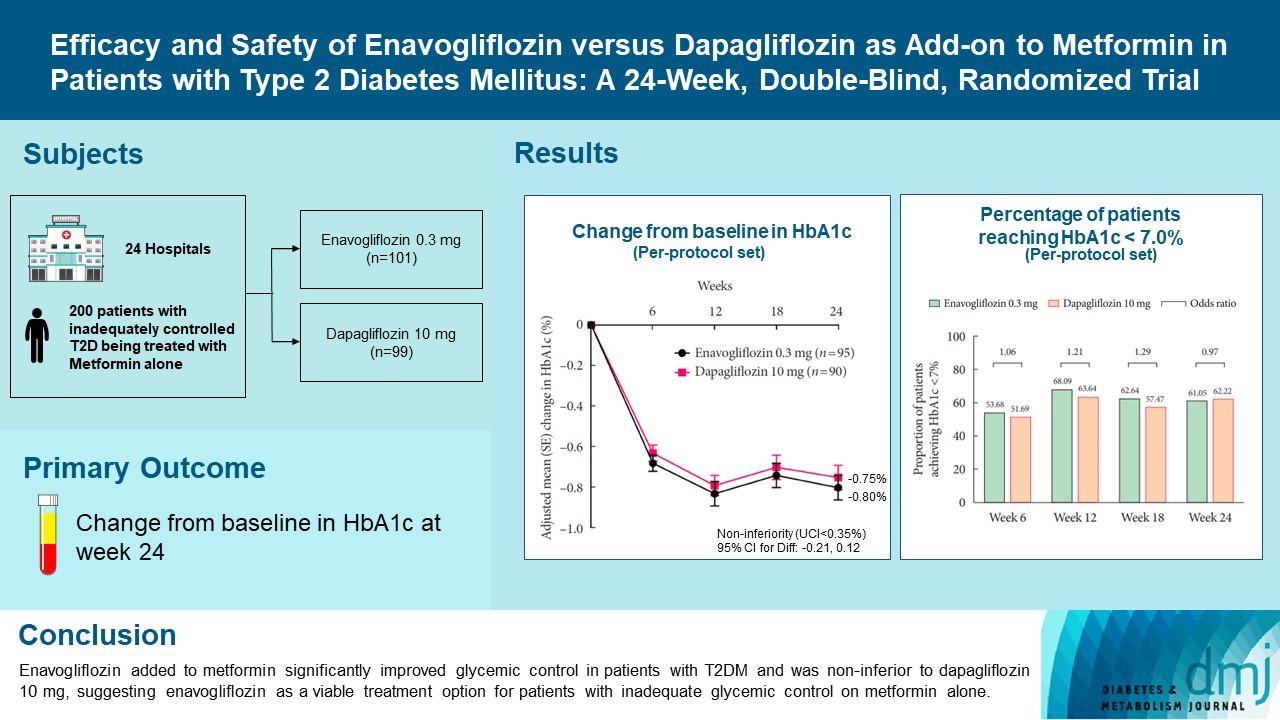
- Efficacy and Safety of Enavogliflozin versus Dapagliflozin as Add-on to Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week, Double-Blind, Randomized Trial
- Kyung Ah Han, Yong Hyun Kim, Doo Man Kim, Byung Wan Lee, Suk Chon, Tae Seo Sohn, In Kyung Jeong, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Jang Won Son, Jae Jin Nah, Hwa Rang Song, Seong In Cho, Seung-Ah Cho, Kun Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):796-807. Published online February 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0315
- 40,156 View
- 576 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Enavogliflozin is a novel sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor currently under clinical development. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin as an add-on to metformin in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) against dapagliflozin.
Methods
In this multicenter, double-blind, randomized, phase 3 study, 200 patients were randomized to receive enavogliflozin 0.3 mg/day (n=101) or dapagliflozin 10 mg/day (n=99) in addition to ongoing metformin therapy for 24 weeks. The primary objective of the study was to prove the non-inferiority of enavogliflozin to dapagliflozin in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) change at week 24 (non-inferiority margin of 0.35%) (Clinical trial registration number: NCT04634500).
Results
Adjusted mean change of HbA1c at week 24 was –0.80% with enavogliflozin and –0.75% with dapagliflozin (difference, –0.04%; 95% confidence interval, –0.21% to 0.12%). Percentages of patients achieving HbA1c <7.0% were 61% and 62%, respectively. Adjusted mean change of fasting plasma glucose at week 24 was –32.53 and –29.14 mg/dL. An increase in urine glucose-creatinine ratio (60.48 vs. 44.94, P<0.0001) and decrease in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (–1.85 vs. –1.31, P=0.0041) were significantly greater with enavogliflozin than dapagliflozin at week 24. Beneficial effects of enavogliflozin on body weight (–3.77 kg vs. –3.58 kg) and blood pressure (systolic/diastolic, –5.93/–5.41 mm Hg vs. –6.57/–4.26 mm Hg) were comparable with those of dapagliflozin, and both drugs were safe and well-tolerated.
Conclusion
Enavogliflozin added to metformin significantly improved glycemic control in patients with T2DM and was non-inferior to dapagliflozin 10 mg, suggesting enavogliflozin as a viable treatment option for patients with inadequate glycemic control on metformin alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin vs. dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on renal function: a pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials
Young Sang Lyu, Sangmo Hong, Si Eun Lee, Bo Young Cho, Cheol-Young Park
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A 52‐week efficacy and safety study of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin as an add‐on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: ENHANCE‐M extension study
Tae Seo Sohn, Kyung‐Ah Han, Yonghyun Kim, Byung‐Wan Lee, Suk Chon, In‐Kyung Jeong, Eun‐Gyoung Hong, Jang Won Son, JaeJin Na, Jae Min Cho, Seong In Cho, Wan Huh, Kun‐Ho Yoon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of renal function on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of enavogliflozin, a potent and selective sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitor, in type 2 diabetes
Sae Im Jeong, Mu Seong Ban, Jun‐Gi Hwang, Min‐Kyu Park, Soo Lim, Sejoong Kim, Soon Kil Kwon, Yoonjin Kim, Jae Min Cho, Jae Jin Na, Wan Huh, Jae‐Yong Chung
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of novel sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor enavogliflozin in type-2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, B.G. Harish, Beatrice Anne, Lakshmi Nagendra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(8): 102816. CrossRef - Characteristics of the Latest Therapeutic Agent for Diabetes
Nuri Yun
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 148. CrossRef - Prospects of using sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors in patients with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)
Iryna Kostitska, Nadia Protas, Liliia Petrovska
Diabetes Obesity Metabolic Syndrome.2023; (5): 8. CrossRef - Navigating the Future of Diabetes Treatment with New Drugs: Focusing on the Possibilities and Prospects of Enavogliflozin
Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 769. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin vs. dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on renal function: a pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials
- Drug/Regimen
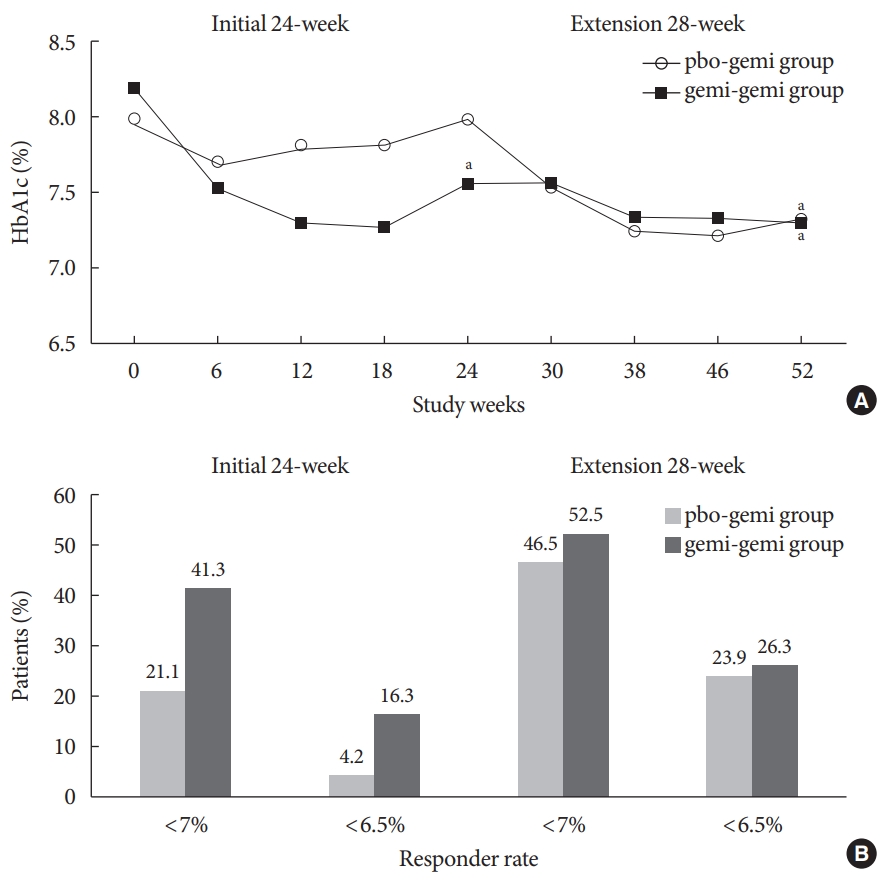
- A Multicentre, Multinational, Open-Label, 52-Week Extension Study of Gemigliptin (LC15-0444) Monotherapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Sae Jeong Yang, Kyung Wan Min, Sandeep Kumar Gupta, Joong Yeol Park, Vyankatesh K.Shivane, Pankaj Kumar Agarwal, Doo Man Kim, Yong Seung Kim, Sei Hyun Baik
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):606-612. Published online September 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0047
- 5,051 View
- 139 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The purpose of this extension study was to assess the long-term efficacy and safety of gemigliptin 50 mg in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Patients with T2DM who had completed the initial 24-week study comparing gemigliptin monotherapy with placebo were eligible to enrol. In the open-label, 28-week extension study, all enrolled patients received gemigliptin, regardless of the treatment received during the initial 24-week study period. The mean reduction±standard deviation (SD) in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) observed after 24 weeks of treatment (–0.6%±1.1%) was further decreased for the gemi-gemi group and the mean change in HbA1c at week 52 from baseline was –0.9%±1.2% (P<0.0001). For the pbo-gemi group, HbA1c decreased after they were switched to gemigliptin, and the mean change in HbA1c at week 52 from baseline was –0.7%±1.2% (P<0.0001). Furthermore, the overall incidence of adverse events demonstrated that gemigliptin was safe and well tolerated up to 52 weeks.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin added to metformin plus gemigliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind, randomized, comparator-active study: ENHANCE-D study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Kyung Ah Han, Tae Nyun Kim, Cheol-Young Park, Jung Hwan Park, Sang Yong Kim, Yong Hyun Kim, Kee Ho Song, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Sik Kim, Gwanpyo Koh, Jun Goo Kang, Mi Kyung Kim, Ji Min Han, Nan Hee Kim, Ji Oh Mok, Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Lim, Sang S
Diabetes & Metabolism.2023; 49(4): 101440. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin added to metformin plus gemigliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A double-blind, randomized, comparator-active study: ENHANCE-D study
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Tae Jung Oh, Jae Myung Yu, Kyung Wan Min, Hyun Shik Son, Moon Kyu Lee, Kun Ho Yoon, Young Duk Song, Joong Yeol Park, In Kyung Jeong, Bong Soo Cha, Yong Seong Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, In Joo Kim, Doo Man Kim, Sung Rae Kim, Kwan Woo Lee, Jeong Hyung Park, In Kyu Lee, Tae Sun Park, Sung Hee Choi, Sung Woo Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(3):276-286. Published online December 7, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0051
- 7,077 View
- 99 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Combination of metformin to reduce the fasting plasma glucose level and an α-glucosidase inhibitor to decrease the postprandial glucose level is expected to generate a complementary effect. We compared the efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose combination of voglibose plus metformin (vogmet) with metformin monotherapy in drug-naïve newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods A total of 187 eligible patients aged 20 to 70 years, with a glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level of 7.0% to 11.0%, were randomized into either vogmet or metformin treatments for 24 weeks. A change in the HbA1c level from baseline was measured at week 24.
Results The reduction in the levels of HbA1c was −1.62%±0.07% in the vogmet group and −1.31%±0.07% in the metformin group (
P =0.003), and significantly more vogmet-treated patients achieved the target HbA1c levels of <6.5% (P =0.002) or <7% (P =0.039). Glycemic variability was also significantly improved with vogmet treatment, estimated by M-values (P =0.004). Gastrointestinal adverse events and hypoglycemia (%) were numerically lower in the vogmet-treated group. Moreover, a significant weight loss was observed with vogmet treatment compared with metformin (−1.63 kg vs. −0.86 kg,P =0.039).Conclusion Vogmet is a safe antihyperglycemic agent that controls blood glucose level effectively, yields weight loss, and is superior to metformin in terms of various key glycemic parameters without increasing the risk of hypoglycemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Phytochemical analysis and antihyperglycemic activity of Castilleja arvensis
Mónica Aideé Díaz-Román, Juan José Acevedo-Fernández, Gabriela Ávila-Villarreal, Elizabeth Negrete-León, A. Berenice Aguilar-Guadarrama
Fitoterapia.2024; 174: 105839. CrossRef - YAP/TAZ axis was involved in the effects of metformin on breast cancer
Yu Xu, Hongke Cai, Yuanfeng Xiong, Li Tang, Longjiang Li, Li Zhang, Yi Shen, Yongqiang Yang, Ling Lin, Jiayi Huang
Journal of Chemotherapy.2023; 35(7): 627. CrossRef - Diabetes remission: Myth or reality?
Ashok Kumar, ShubhaLaxmi Margekar, Ravi Kumar
Indian Journal of Medical Specialities.2023; 14(1): 3. CrossRef - Analysis of Reports Sent to the Portuguese Pharmacovigilance System and Published Literature Regarding the Safety of Metformin in the Elderly
Beatriz Esteves, Cristina Monteiro, Ana Paula Coelho Duarte
Healthcare.2023; 11(15): 2197. CrossRef - Rapid prediction method of α-Glycosidase inhibitory activity of Coreopsis tinctoria extract from different habitats by near infrared spectroscopy
Xiaogang He, Xiang Han, Jiaping Yu, Yulong Feng, Ganghui Chu
Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy.2022; 268: 120601. CrossRef - Insulin autoimmune syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes: A report of two cases
Y. Shin, T.J. Oh, S.H. Choi, H.C. Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism.2021; 47(1): 101115. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Treatment with Quadruple Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Multi-Center, Retrospective, Observational Study
Jun Sung Moon, Sunghwan Suh, Sang Soo Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Jeong Mi Kim, Min Hee Jang, Kyung Ae Lee, Ju Hyung Lee, Seung Min Chung, Young Sang Lyu, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jung Eun Jang, Tae Nyun Kim, Sung Woo Kim, Eonju Jeon, Nan Hee Cho, Mi-Kyung Ki
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 675. CrossRef - Quantifying Remission Probability in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Sanjay Kalra, Ganapathi Bantwal, Nitin Kapoor, Rakesh Sahay, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Beatrice Anne, Raju A Gopal, Sunil Kota, Ashok Kumar, Ameya Joshi, Debmalya Sanyal, Mangesh Tiwaskar, Ashok Kumar Das
Clinics and Practice.2021; 11(4): 850. CrossRef - The effect of voglibose on metabolic profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials
Peyman Nowrouzi-Sohrabi, Reza Tabrizi, Shahla Rezaei, Fatemeh Jafari, Kamran Hessami, Mehdi Abedi, Mohammad Jalali, Pedram Keshavarzi, Saeed Shahabi, Ali Asghar Kolahi, Kristin Carson-Chahhoud, Amirhossein Sahebkar, Saeid Safiri
Pharmacological Research.2020; 159: 104988. CrossRef - Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Metabolism of Voglibose In Vitro and In Vivo
Mahesh Raj Nepal, Mi Jeong Kang, Geon Ho Kim, Dong Ho Cha, Ju-Hyun Kim, Tae Cheon Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 908. CrossRef - Response: Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes metab J 2019;43;276-86)
Tae Jung Oh, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 547. CrossRef - Letter: Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43;276-86)
Hannah Seok, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 545. CrossRef
- Phytochemical analysis and antihyperglycemic activity of Castilleja arvensis
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Effects of Lobeglitazone, a Novel Thiazolidinedione, on Bone Mineral Density in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus over 52 Weeks
- Soo Lim, Kyoung Min Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Doo Man Kim, Jeong-Taek Woo, Choon Hee Chung, Kyung Soo Ko, Jeong Hyun Park, Yongsoo Park, Sang Jin Kim, Hak Chul Jang, Dong Seop Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(5):377-385. Published online October 24, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.5.377
- 4,275 View
- 42 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The aim of this multicenter, randomized, double-blind study was to examine the effect of lobeglitazone, a novel thiazolidinedione, on the changes in bone mineral density (BMD) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods A 24-week, double-blinded phase was followed by a 28-week, open-label phase, in which the placebo group also started to receive lobeglitazone. A total of 170 patients aged 34 to 76 years were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive lobeglitazone 0.5 mg or a matching placebo orally, once daily. BMD was assessed using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry at week 24 and at the end of the study (week 52).
Results During the double-blinded phase, the femur neck BMD showed decreasing patterns in both groups, without statistical significance (−0.85%±0.36% and −0.78%±0.46% in the lobeglitazone and placebo groups, respectively). The treatment difference between the groups was 0.07%, which was also not statistically significant. Further, minimal, nonsignificant decreases were observed in both groups in the total hip BMD compared to values at baseline, and these differences also did not significantly differ between the groups. During the open-label phase, the BMD was further decreased, but not significantly, by −0.32% at the femur neck and by −0.60% at the total hip in the lobeglitazone group, and these changes did not significantly differ compared with the original placebo group switched to lobeglitazone.
Conclusion Our results indicate that treatment with lobeglitazone 0.5 mg over 52 weeks showed no detrimental effect on the BMD compared to the placebo.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of novel thiazolidinedione lobeglitazone for managing type-2 diabetes a meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Manoj Kumar, Priyankar K. Datta, Ritin Mohindra, Meha Sharma
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(1): 102697. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of lobeglitazone, a new Thiazolidinedione, as compared to the standard of care in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Shashank R. Joshi, Saibal Das, Suja Xaviar, Shambo Samrat Samajdar, Indranil Saha, Sougata Sarkar, Shatavisa Mukherjee, Santanu Kumar Tripathi, Jyotirmoy Pal, Nandini Chatterjee
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(1): 102703. CrossRef - The benefits of adipocyte metabolism in bone health and regeneration
Lisa-Marie Burkhardt, Christian H. Bucher, Julia Löffler, Charlotte Rinne, Georg N. Duda, Sven Geissler, Tim J. Schulz, Katharina Schmidt-Bleek
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Will lobeglitazone rival pioglitazone? A systematic review and critical appraisal
Kalyan Kumar Gangopadhyay, Awadhesh Kumar Singh
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(4): 102747. CrossRef - Comparison of therapeutic efficacy and safety of sitagliptin, dapagliflozin, or lobeglitazone adjunct therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on sulfonylurea and metformin: Third agent study
Jun Hwa Hong, Jun Sung Moon, Kayeon Seong, Soo Lim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110872. CrossRef - Bone Mineral Density Evaluation Among Type 2 Diabetic Patients in Rural Haryana, India: An Analytical Cross-Sectional Study
Nitish Khandelwal, Surbhi Rajauria, Siddhesh Pandurang Kanjalkar, Omkar Shivaji Chavanke, Sanjay Rai
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lobeglitazone and Its Therapeutic Benefits: A Review
Balamurugan M, Sarumathy S, Robinson R
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A double‐blind, Randomized controlled trial on glucose‐lowering EFfects and safety of adding 0.25 or 0.5 mg lobeglitazone in type 2 diabetes patients with INadequate control on metformin and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor therapy: REFIND study
Soree Ryang, Sang Soo Kim, Ji Cheol Bae, Ji Min Han, Su Kyoung Kwon, Young Il Kim, Il Seong Nam‐Goong, Eun Sook Kim, Mi‐kyung Kim, Chang Won Lee, Soyeon Yoo, Gwanpyo Koh, Min Jeong Kwon, Jeong Hyun Park, In Joo Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(9): 1800. CrossRef - A Real-World Study of Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Lobeglitazone in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Bo-Yeon Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Suk Kyeong Kim, Jung-Hyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Hyeong-Kyu Park, Kee-Ho Song, Jong Chul Won, Jae Myung Yu, Mi Young Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Lim, Sung Wan Chun, In-Kyung Jeong, Choon Hee Chung, Seung Jin Han, Hee-Seok Kim, Ju-Y
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 855. CrossRef - Comparative Efficacy of Lobeglitazone Versus Pioglitazone on Albuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(1): 171. CrossRef - Lobeglitazone: A Novel Thiazolidinedione for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jaehyun Bae, Taegyun Park, Hyeyoung Kim, Minyoung Lee, Bong-Soo Cha
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 326. CrossRef - Effect of lobeglitazone on motor function in rat model of Parkinson’s disease with diabetes co-morbidity
Kambiz Hassanzadeh, Arman Rahimmi, Mohammad Raman Moloudi, Rita Maccarone, Massimo Corbo, Esmael Izadpanah, Marco Feligioni
Brain Research Bulletin.2021; 173: 184. CrossRef - Recent Perspective on Thiazolidinedione
Won Jun Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(2): 97. CrossRef - Use of in vitro bone models to screen for altered bone metabolism, osteopathies, and fracture healing: challenges of complex models
Sabrina Ehnert, Helen Rinderknecht, Romina H. Aspera-Werz, Victor Häussling, Andreas K. Nussler
Archives of Toxicology.2020; 94(12): 3937. CrossRef - Update on: effects of anti-diabetic drugs on bone metabolism
Guillaume Mabilleau, Béatrice Bouvard
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2020; 15(6): 415. CrossRef - The use of metformin, insulin, sulphonylureas, and thiazolidinediones and the risk of fracture: Systematic review and meta‐analysis of observational studies
Khemayanto Hidayat, Xuan Du, Meng‐Jiao Wu, Bi‐Min Shi
Obesity Reviews.2019; 20(10): 1494. CrossRef - Diabetes pharmacotherapy and effects on the musculoskeletal system
Evangelia Kalaitzoglou, John L. Fowlkes, Iuliana Popescu, Kathryn M. Thrailkill
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Morin Exerts Anti‐Arthritic Effects by Attenuating Synovial Angiogenesis via Activation of Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor‐γ
Mengfan Yue, Ni Zeng, Yufeng Xia, Zhifeng Wei, Yue Dai
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of diabetes therapy on bone: A clinical perspective
Karim G. Kheniser, Carmen M. Polanco Santos, Sangeeta R. Kashyap
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2018; 32(7): 713. CrossRef - Changes in the Bone Mineral Density of Femur Neck and Total Hip Over a 52-Week Treatment with Lobeglitazone
Da Young Lee, Ji A Seo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 374. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of novel thiazolidinedione lobeglitazone for managing type-2 diabetes a meta-analysis
- Prevalence of Chronic Complications in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on the Korean National Diabetes Program
- Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Mi Kwang Kwon, Ie Byung Park, Kyu Jeung Ahn, In Ju Kim, Sung-Hoon Kim, Hyoung Woo Lee, Kyung Soo Koh, Doo Man Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kwan Woo Lee, Moon Suk Nam, Yong Soo Park, Jeong-taek Woo, Young Seol Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(5):504-512. Published online October 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.5.504
- 4,572 View
- 39 Download
- 52 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The Korean National Diabetes Program (KNDP) cohort study is performing an ongoing large-scale prospective multicenter investigation to discover the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes in Korean patients. This study was performed to examine the prevalence of chronic complications in patients with type 2 diabetes among those registered in the KNDP cohort within the past 4 years.
Methods This study was performed between June 2006 and September 2009 at 13 university hospitals and included 4,265 KNDP cohort participants. Among the participants, the crude prevalence of microvascular and macrovascular diseases of those checked for diabetes-related complications was determined, and the adjusted standard prevalence and standardization of the general population prevalence ratio (SPR) was estimated based on the 2005 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) population demographics.
Results Among the KNDP registrants, 43.2% had hypertension, 34.8% had dyslipidemia, 10.8% had macrovascular disease, and 16.7% had microvascular disease. The SPR of the KNDP registrants was significantly higher than that of the KNHANES subjects after adjusting for demographics in the KNHANES 2005 population. However, with the exception of cardiovascular disease in females, the standardized prevalence for the most complicated items in the survey was significantly higher than that in the KNHANES subjects.
Conclusion The prevalence of macrovascular disease and peripheral vascular disease were significantly higher in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes than in the normal population. However, no significant difference was noted in the prevalence of cardiovascular disease in females.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of diabetes distress on glycemic control and diabetic complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hye-Sun Park, Yongin Cho, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, Young Ju Suh, Suk Chon, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Kwan Woo Lee, So Hun Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and economic impact of changing reimbursement criteria for statin treatment among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in South Korea
Siin Kim, Kyungseon Choi, Ji-yool Kim, Hae Sun Suh
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Promising First Cohort Study in Korean Patients with Obesity and Overweight: Gangwon Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome Study
Eun-Jung Rhee
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2022; 31(4): 285. CrossRef - Impact of noncommunicable disease conditions and physical burden on intent to leave midwifery in Hungary
Krisztina Éles Gebriné, Kinga Lampek, Péter Takács, Miklós Zrínyi, Attila Sárváry, Andrea Sárváry
Kontakt.2021; 23(1): 45. CrossRef - Dietary glutamic acid and aspartic acid as biomarkers for predicting diabetic retinopathy
So Young Park, Jieun Kim, Jung Il Son, Sang Youl Rhee, Do-Yeon Kim, Suk Chon, Hyunjung Lim, Jeong-Taek Woo
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)
Ja Young Jeon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 613. CrossRef - Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)
Kyoung Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyeong Jin Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 617. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics and Prevalence of Comorbidities according to Metformin Use in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Sang Ouk Chin, In Gyoon Ha, Sang Youl Rhee, Su Jin Jeong, Suk Chon, Sung Hoon Kim, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Moon Suk Nam, Kwan Woo Lee, Jeong Taek Woo
International Journal of Endocrinology.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Perioperative anesthetic management of patients with diabetes mellitus: focused on blood glucose control
Hyungseok Seo
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2020; 63(9): 526. CrossRef - Predicting Old-age Mortality Using Principal Component Analysis: Results from a National Panel Survey in Korea
Jaeyong Shin, Kwang-Soo Lee, Jae-Hyun Kim
Medicina.2020; 56(7): 360. CrossRef - A relationship between endoscopic findings
and diabetic regulation, and complications in patients with diabetes mellitus
Sevki Konur
Archives of Medical Science – Civilization Diseases.2020; 5(1): 53. CrossRef - Randomized control trial comparing the effect of cilostazol and aspirin on changes in carotid intima-medial thickness
Sangmo Hong, Munsuk Nam, Bertis B. Little, Seihyun Paik, Kwanwoo Lee, Jungtaek Woo, Dooman Kim, Jungoo Kang, Minyoung Chun, Yongsoo Park
Heart and Vessels.2019; 34(11): 1758. CrossRef - Genome‐wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for diabetic nephropathy in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Kyung H. Jeong, Jin S. Kim, Jeong‐Taek Woo, Sang Y. Rhee, Yu H. Lee, Yang G. Kim, Ju‐Young Moon, Su K. Kim, Sun W. Kang, Sang H. Lee, Yeong H. Kim
Clinical Genetics.2019; 96(1): 35. CrossRef - Presence of Carotid Plaque Is Associated with Rapid Renal Function Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Normal Renal Function
Da Hea Seo, So Hun Kim, Joon Ho Song, Seongbin Hong, Young Ju Suh, Seong Hee Ahn, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Kwan Woo Lee, Young Seol Kim, Moonsuk Nam
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 840. CrossRef - The relationship between demographic and anthropometric characteristics and diabetic complications and number of hospitalizations in hospitalized diabetic patients
Yusuf Kayar, Mehmet Agin
Archives of Medical Science – Civilization Diseases.2019; 4(1): 7. CrossRef - Importance of family history of diabetes in computing a diabetes risk score in Korean prediabetic population
Morena Ustulin, Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Kyu Keung Ahn, Ji Eun Lim, Bermseok Oh, Sung-Hoon Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Moon Suk Nam, Kwan Woo Lee, Young Seol Kim, Jeong-Taek Woo
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Characteristics of frequent emergency department users with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korea
Morena Ustulin, Junghoon Woo, Jeong‐taek Woo, Sang Youl Rhee
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2018; 9(2): 430. CrossRef - Implementation of the Chronic Disease Care System and its association with health care costs and continuity of care in Korean adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Woorim Kim, Yoon Soo Choy, Sang Ah Lee, Eun-Cheol Park
BMC Health Services Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Long‐term effects on glycaemic control and β‐cell preservation of early intensive treatment in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A multicentre randomized trial
Suk Chon, Sang Youl Rhee, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Moon Suk Nam, Kwan Woo Lee, Soon Jib Yoo, Gwanpyo Koh, Dae Ho Lee, Young Seol Kim, Jeong‐Taek Woo
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2018; 20(5): 1121. CrossRef - Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index as a Surrogate Marker of Early Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in Koreans with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
So Young Park, Sang Ook Chin, Sang Youl Rhee, Seungjoon Oh, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sung Woon Kim, Suk Chon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(4): 285. CrossRef - Metformin reduces the risk of cancer in patients with type 2 diabetes
Hae Jin Kim, SooJin Lee, Ki Hong Chun, Ja Young Jeon, Seung Jin Han, Dae Jung Kim, Young Seol Kim, Jeong-Taek Woo, Moon-Suk Nam, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Kwan Woo Lee
Medicine.2018; 97(8): e0036. CrossRef - Impact of Socioeconomic Status on Health Behaviors, Metabolic Control, and Chronic Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
So Hun Kim, Seung Youn Lee, Chei Won Kim, Young Ju Suh, Seongbin Hong, Seong Hee Ahn, Da Hae Seo, Moon-Suk Nam, Suk Chon, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Kwan Woo Lee, Young Seol Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(5): 380. CrossRef - Failure of monotherapy in clinical practice in patients with type 2 diabetes: The Korean National Diabetes Program
Ja Young Jeon, Soo Jin Lee, Sieun Lee, Soo Jin Kim, Seung Jin Han, Hae Jin Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Young Seol Kim, Jeong Taek Woo, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Moonsuk Nam, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Kwan‐Woo Lee
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2018; 9(5): 1144. CrossRef - Prediction of Coronary Heart Disease Risk in Korean Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Bo Kyung Koo, Sohee Oh, Yoon Ji Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2018; 7(2): 110. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Management of Diabetic Foot
Chang Won Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(3): 168. CrossRef - Clinical characteristics and risk factors for retinal diabetic neurodegeneration in type 2 diabetes
Kiyoung Kim, Eung Suk Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Jeong-taek Woo, Seung-Young Yu
Acta Diabetologica.2017; 54(11): 993. CrossRef - Features of Long-Standing Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy: A Study Based on Standardized Clinical Data
Sejeong Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Su Jin Jeong, Kiyoung Kim, Suk Chon, Seung-Young Yu, Jeong-Taek Woo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 393. CrossRef - Clinical heterogeneity of type 1 diabetes (T1D) found in Asia
Yongsoo Park, Kupper A. Wintergerst, Zhiguang Zhou
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Response: Features of Long-Standing Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy: A Study Based on Standardized Clinical Data (Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:393-404)
Sang Youl Rhee, Jeong-Taek Woo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(6): 494. CrossRef - Current status of managing diabetes mellitus in Korea
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(5): 845. CrossRef - Hypoglycemia is associated with dementia in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: An analysis based on the Korea National Diabetes Program Cohort
Sang Ouk Chin, Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Moon Suk Nam, Kwan Woo Lee, Ki Hong Chun, Jeong-taek Woo, Young Seol Kim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2016; 122: 54. CrossRef - Relationship between fruit and fish intakes and cardiovascular disease risk factors in Korean women with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Based on the 4th and 5th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
Ji Soo Oh, Hyesook Kim, Ki Nam Kim, Namsoo Chang
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2016; 49(5): 304. CrossRef - Hypoglycemia and Medical Expenses in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Analysis Based on the Korea National Diabetes Program Cohort
Sang Youl Rhee, Soo Min Hong, Suk Chon, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Sung Hoon Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Yong Soo Park, Moon Suk Nam, Kwan Woo Lee, Jeong-Taek Woo, Young Seol Kim, Zhengdong Zhang
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(2): e0148630. CrossRef - Elevated lipoprotein(a) levels predict cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 10-year prospective cohort study
Tae-Seok Lim, Jae-Seung Yun, Seon-Ah Cha, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Dong Yoo, Yu-Bae Ahn, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(6): 1110. CrossRef - Low Economic Status Is Identified as an Emerging Risk Factor for Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Men Aged 30 to 59 Years in Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008 to 2010
Bo Kyung Koo, Sang Wan Kim, Ka Hee Yi, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(2): 137. CrossRef - Assessment of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with metformin–sulfonylurea combination: Results of a multicenter, cross‐sectional, observational study in Korea
Sin Gon Kim, Jong Ryeal Hahm, Duk Kyu Kim, Sung Rae Cho, Dong Seop Choi
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2015; 6(3): 317. CrossRef - Clinical and Economic Outcomes in Medication-Adherent and -Nonadherent Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in the Republic of Korea
So-Yeon An, Hae Jin Kim, Ki Hong Chun, Tae Ho Kim, Ja Young Jeon, Dae Jung Kim, Seung Jin Han, Young Seol Kim, Jeong Taek Woo, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Yongsoo Park, Moonsuk Nam, Sei Hyun Baik, Kwan-Woo Lee
Clinical Therapeutics.2014; 36(2): 245. CrossRef - Serum Magnesium Level Is Associated with Type 2 Diabetes in Women with a History of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: The Korea National Diabetes Program Study
Sae Jeong Yang, Soon Young Hwang, Sei Hyun Baik, Kwan Woo Lee, Moon Suk Nam, Yong Soo Park, Jeong Taek Woo, Young Seol Kim, Sunmin Park, So-Young Park, Chang Hoon Yim, Hyun Koo Yoon, Sung-Hoon Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2014; 29(1): 84. CrossRef - Heart rate variability in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus
Camila Balsamo Gardim, Bruno Affonso P. de Oliveira, Aline Fernanda B. Bernardo, Rayana Loch Gomes, Francis Lopes Pacagnelli, Roselene Modolo R. Lorençoni, Luiz Carlos M. Vanderlei
Revista Paulista de Pediatria.2014; 32(2): 279. CrossRef - Development of an HbA1c-Based Conversion Equation for Estimating Glycated Albumin in a Korean Population with a Wide Range of Glucose Intolerance
Chang Hee Jung, You-Cheol Hwang, Kwang Joon Kim, Bong Soo Cha, Cheol-Young Park, Won Seon Jeon, Jae Hyeon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Sang Youl Rhee, Jeong-taek Woo, Byung-Wan Lee, Sompop Bencharit
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(4): e95729. CrossRef - It's Still Not Too Late to Make a Change: Current Status of Glycemic Control in Korea
Sang Yong Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(3): 194. CrossRef - Prevalence and factors associated with diabetic retinopathy in a Korean adult population: The 2008–2009 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ju Yean Yang, Na Kyung Kim, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung Hyun Noh, Dae Jung Kim, Kyung Soo Ko, Byoung Doo Rhee, Dong-Jun Kim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2013; 102(3): 218. CrossRef - Increasing achievement of the target goals for glycemic, blood pressure and lipid control for adults with diagnosed diabetes in Korea
Sung Hoon Yu, Jun Goo Kang, Yoo‐Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Hyung Joon Yoo, Hong Yup Ahn, Sung Woo Park, Cheol‐Young Park
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2013; 4(5): 460. CrossRef - Hemoglobin A1c May Be an Inadequate Diagnostic Tool for Diabetes Mellitus in Anemic Subjects
Jung Il Son, Sang Youl Rhee, Jeong-taek Woo, Jin Kyung Hwang, Sang Ouk Chin, Suk Chon, Seungjoon Oh, Sung Woon Kim, Young Seol Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(5): 343. CrossRef - Implication of circulating omentin-1 level on the arterial stiffening in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hye Jin Yoo, Soon Young Hwang, Ho Cheol Hong, Hae Yoon Choi, Sae Jeong Yang, Kwan Woo Lee, Moon Suk Nam, Yong Soo Park, Jeong Taek Woo, Young Seol Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik
Endocrine.2013; 44(3): 680. CrossRef - Comparison of Two Creatinine-Based Equations for Predicting Decline in Renal Function in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Nephropathy in a Korean Population
Eun Young Lee, Young-Mi Lee, Kyu Hun Choi, Hyun Chul Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Beom Seok Kim
International Journal of Endocrinology.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef - Association between Nutrient Intake and Obesity in Type 2 Diabetic Patients from the Korean National Diabetes Program: A Cross-Sectional Study
So Hun Kim, Seong Bin Hong, Young Ju Suh, Yun Jin Choi, Moonsuk Nam, Hyoung Woo Lee, Ie Byung Park, Suk Chon, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Dae Jung Kim, Kwan Woo Lee, Young Seol Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2012; 27(10): 1188. CrossRef - C1q/TNF-Related Protein-3 (CTRP-3) and Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF) Concentrations in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome
Kyung Mook Choi, Soon Young Hwang, Ho Cheol Hong, Sae Jeong Yang, Hae Yoon Choi, Hye Jin Yoo, Kwan Woo Lee, Moon Suk Nam, Yong Soo Park, Jeong Taek Woo, Young Seol Kim, Dong Seop Choi, Byung-Soo Youn, Sei Hyun Baik
Diabetes.2012; 61(11): 2932. CrossRef - Direct Medical Costs for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Related Complications: A Prospective Cohort Study Based on the Korean National Diabetes Program
Tae Ho Kim, Ki Hong Chun, Hae Jin Kim, Seung Jin Han, Dae Jung Kim, Jiyeong Kwak, Young Seol Kim, Jeong Taek Woo, Yongsoo Park, Moonsuk Nam, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Kwan Woo Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2012; 27(8): 876. CrossRef - Epidemiology of Micro- and Macrovascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes in Korea
Jung Hee Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(6): 571. CrossRef - Letter: The Prevalence of Peripheral Arterial Disease in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Attending a University Hospital (Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:543-50)
Won Jun Kim, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(6): 637. CrossRef - Satisfaction with High Deductible Policies among Patients with Diabetes in the Korean General/University Hospital System
Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Diabetes.2011; 12(4): 179. CrossRef
- Impact of diabetes distress on glycemic control and diabetic complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Regulation of Glucose Control in People with Type 2 Diabetes: A Review and Consensus
- Jeong-Taek Woo, Kyung Soo Park, Dong-Won Byun, Kyung Soo Ko, Yoon-Sok Chung, Doo Man Kim, Tae Sun Park, Bong Soo Cha, In Kyu Lee, Joong Yeol Park, Hyun Shik Son, Moon-Kyu Lee, Kwang Won Kim, Ho Young Son
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(1):16-20. Published online February 28, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.1.16
- 3,378 View
- 47 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader A conference was convened by the Korean Diabetes Association and the Korean Endocrine Society on September 7, 2009 to discuss and organize the results of research on intensive glucose control for the prevention of cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Professor Kyung Soo Park led the conference, and Professors Kwang Won Kim and Ho Young Son acted as chairmen. Professors Doo Man Kim, Tae Sun Park, and Bong Soo Cha reported on intensive glucose control and diabetic complications, including the UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS), Diabetes Control and Complication Trial (DCCT) research results, the recently published Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD), Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: Preterax and Diamicron Modified Release Controlled Evaluation (ADVANCE), and Veterans Affairs Diabetes Trial (VADT) research, as well as meta-analyses. Professor Jeong-Taek Woo reported on the manuscript written by the committee for the Korean Diabetes Association which dealt with the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Professors Kyung Soo Ko, Joong Yeol Park, Hyun Shik Son, Moon-Kyu Lee, Dong-Won Byun, and Yoon-Sok Chung participated in the discussion and collected information for the manuscript from all of the participants. The aim of the debate was to determine how to establish target goals for intensive glucose control and how to individualize those goals. The participants concluded that there was no need to modify the recommendation of maintaining an HbA1c under 6.5%, the current blood glucose treatment goal that is recommended by the Korean Diabetes Association. In addition, individual target goals for glucose control were recommended depending on the situation of each patient. We report on the consensus statement from the meeting.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Long-term quality-of-care score for predicting the occurrence of acute myocardial infarction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Pi-I Li, How-Ran Guo
World Journal of Diabetes.2023; 14(7): 1091. CrossRef
- Long-term quality-of-care score for predicting the occurrence of acute myocardial infarction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Relationship Between Metabolic Syndrome and Risk of Chronic Complications in Koreans with Type 2 Diabetes.
- Hye Soo Chung, Ji A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Doo Man Kim, Choon Hee Chung, Dong seop Choi
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(5):392-400. Published online October 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.5.392
- 2,040 View
- 26 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
We examined the relationships between components of metabolic syndrome at the time of diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, and the development of chronic complications in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes. METHODS: The medical records of patients with type 2 diabetes who had undergone treatment for at least five years prior were collected from 10 general hospitals in Korea. Among a total of 1,418 patients reviewed for possible inclusion in this study, 603 patients were selected, and the occurrence of complications among these patients was evaluated. RESULTS: Among the 603 patients (male, 253; female, 350), 154 males (60.8%) and 266 females (76.0%) were diagnosed with metabolic syndrome at the time of initial diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. The incidence of chronic complications (average follow-up 15.2 +/- 4.9 years) included 60 cases of coronary artery disease (CAD), 57 cases of cerebrovascular accident (CVA), 268 cases of diabetic retinopathy (DR), 254 cases of diabetic nephropathy (DN), and 238 cases of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN). As compared to patients without metabolic syndrome, the adjusted relative risks (95% CI) of incidental diabetic complications in patients with metabolic syndrome were 3.28 (1.40~7.71) for CAD, 2.04 (0.86~4.82) for CVA, 1.53 (1.10~2.14) for DR, 1.90 (1.29~2.80) for DN, and 1.51, (1.06~2.14) for DPN. With the addition of just one constituent of metabolic syndrome, the relative risk of developing CAD, CVD, DR, DN, and DPN increased by 2.08 (95% CI, 1.27~3.40), 1.16 (0.80~1.66), 1.09 (0.93~1.26), 1.29 (1.06~1.57) and 1.06 (0.87~1.26), respectively. CONCLUSION: Metabolic syndrome in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes increases the risk of developing both macrovascular and microvascular complications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- COVID-19 pandemic: Effects of national lockdown on the state of health of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Moroccan population
Hamid Farhane, Majida Motrane, Fatima-Ezzahra Anaibar, Aïcha Motrane, Said Nassor Abeid, Nourdin Harich
Primary Care Diabetes.2021; 15(5): 772. CrossRef - Profil clinique du syndrome métabolique et facteurs associés à sa présence au cours du diabète de type 2 à Ouagadougou (Burkina Faso)
O. Guira, H. Tiéno, Y. Sagna, P. Mayodé, D. Yanogo, L. Zoungrana, C.-G. Kyélem, M.-T. Yaméogo, J.-Y. Drabo
Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques.2016; 10(1): 70. CrossRef - The Relationship between Metabolic Syndrome and Quality of Life in Korean Adult Women
Hyung-Su Park, Jong Park
The Journal of the Korea institute of electronic communication sciences.2013; 8(4): 639. CrossRef - Diabetes Risk Analysis Model with Personalized Food Intake Preference
So-Hye Jeon, Nam-Hyun Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2013; 14(11): 5771. CrossRef - Comorbidity Study on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Data Mining
Hye Soon Kim, A Mi Shin, Mi Kyung Kim, Yoon Nyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2012; 27(2): 197. CrossRef - Cardio-Metabolic Features of Type 2 Diabetes Subjects Discordant in the Diagnosis of Metabolic Syndrome
Sa Rah Lee, Ying Han, Ja Won Kim, Ja Young Park, Ji Min Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Mi-Kyoung Park, Hye-Jeong Lee, Duk Kyu Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(5): 357. CrossRef
- COVID-19 pandemic: Effects of national lockdown on the state of health of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Moroccan population
- Effects of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Risk Factors of Acute Coronary Syndrome.
- Hong Ju Moon, Jun Goo Kang, Min Ho Jo, Byung Wan Lee, Cheol Young Park, Seong Jin Lee, Eun Kyung Hong, Jae Myoung Yu, Doo Man Kim, Sung Hee Ihm, Hyun Kyu Kim, Chong Yun Rhim, Moon Gi Choi, Hyung Joon Yoo, Sung Woo Park
- Korean Diabetes J. 2006;30(6):435-441. Published online November 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2006.30.6.435
- 2,298 View
- 18 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is equivalent as well a risk factor of cardiovascular disease. We analyzed the effects of DM on clinical risk factors of acute coronary syndrome by comparing DM group with Non-DM group. METHODS: A total of 847 (514 males and 333 females) patients with acute coronary syndrome was selected from 1664 patients who had undergone coronary angiography (CAG). These patients comprised 105 subjects with non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (MI), 313 with ST elevation MI and 429 with unstable angina. According to the presence of DM, we retrospectively reviewed the measured basic demographics, biochemical markers and coronary angiographic findings. RESULTS: In the multivariated analysis, history of hypertension (P = 0.001), C-reactive protein (CRP) level (P = 0.001) and triglyceride level (P = 0.018) were independent risk factors in type 2 diabetic group. Also the frequency of multiple coronary vessel disease was higher in DM group than non-DM group on the coronary angiographic finding CONCLUSIONS: Classic risk factors for acute coronary syndrome are strong predictors in patients with type 2 DM. Among these factors, the most important powerful risk factor is history of hypertension. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gender-Based Differences in the Management and Prognosis of Acute Coronary Syndrome in Korea
Hee Tae Yu, Kwang Joon Kim, Woo-Dae Bang, Chang-Myung Oh, Ji-Yong Jang, Sung-Soo Cho, Jung-Sun Kim, Young-Guk Ko, Donghoon Choi, Myeong-Ki Hong, Yangsoo Jang
Yonsei Medical Journal.2011; 52(4): 562. CrossRef
- Gender-Based Differences in the Management and Prognosis of Acute Coronary Syndrome in Korea
- Efficacy Evaluation of Atorvastatin in Korean Hyperlipidemic Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
- Dong Seop Choi, Duk Kyu Kim, Doo Man Kim, Seong Yeon Kim, Moon Suk Nam, Yong Soo Park, Ho Sang Shon, Chul Woo Ahn, Kwan Woo Lee, Ki Up Lee, Moon Kyu Lee, Choon Hee Chung, Bong Yeon Cha
- Korean Diabetes J. 2006;30(4):292-302. Published online July 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2006.30.4.292
- 2,084 View
- 20 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
NCEP ATP III Guideline recommends aggressive treatments of diabetic dyslipidemia, recognizing diabetes mellitus as CHD risk equivalents. This study was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of atorvastatin in hyperlipidemic patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus through post-marketing drug use investigation of atorvastatin. METHODS: An open, multi-center, non-comparison, titrated dosage study was conducted in hyperlipidemic patients, who were treated with atorvastatin at first visiting hospitals from Mar. 2004 to Sep. 2004. 96 endocrinologists participated from 66 centers in this study. Total 2,182 hyperlipidemic patients were enrolled and 1,514 patients among them were accompanied by diabetes mellitus. Efficacy was evaluated at later than 4-week treatment by % change of total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL-cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol from baseline. Percent of patients reaching LDL-cholesterol level less than 100 mg/dL was also analyzed. The adverse events incidence and abnormalities of clinical laboratory values were evaluated for safety monitoring. RESULTS: Total cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL-cholesterol level were reduced by 26.6%, 12.0%, and 34.8%, respectively, in diabetic hyperlipidemic patients after atorvastatin treatment. The patients with LDL-cholesterol level of less than 100 mg/dL were increased from 2.8% to 52.6%. Atorvastatin was considered to be safe because adverse drug reactions were reported in 32 patients (1.5%) of total 2,182 patients. CONCLUSION: Atorvastatin was effective and safe in hyperlipidemic patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Response: A Retrospective Study on the Efficacy of a Ten-Milligram Dosage of Atorvastatin for Treatment of Hypercholesterolemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients (Korean Diabetes J 2010;34:359-67)
Dong Kyun Kim, Sa Rah Lee, Min Sik Kim, Suk Hyang Bae, Jin Yeon Hwang, Jung-Min Kim, Sung Hwan Suh, Hye-Jeong Lee, Mi Kyoung Park, Duk Kyu Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(1): 88. CrossRef - A Retrospective Study on the Efficacy of a Ten-Milligram Dosage of Atorvastatin for Treatment of Hypercholesterolemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Dong Kyun Kim, Sa Rah Lee, Min Sik Kim, Suk Hyang Bae, Jin Yeon Hwang, Jung-Min Kim, Sung Hwan Suh, Hye-Jeong Lee, Mi Kyoung Park, Duk Kyu Kim
Korean Diabetes Journal.2010; 34(6): 359. CrossRef - The Association of Plasma HDL-Cholesterol Level with Cardiovascular Disease Related Factors in Korean Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Hye Sook Hong, Jong Suk Park, Han Kyoung Ryu, Wha Young Kim
Korean Diabetes Journal.2008; 32(3): 215. CrossRef
- Response: A Retrospective Study on the Efficacy of a Ten-Milligram Dosage of Atorvastatin for Treatment of Hypercholesterolemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients (Korean Diabetes J 2010;34:359-67)
- Clinical Characteristics and Analysis of Risk Factor for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Diabetic Patient.
- Kwang Hyuk Park, Seong Bo Yoon, Min Ho Jo, Eon Kyung Hong, Seong Jin Lee, In Kyung Jeong, Chul Young Park, Ki Won Oh, Hyun Kyu Kim, Jac Myoung Yu, Doo Man Kim, Sung Hee Lim, Moon Ki Choi, Hyung Jun Yoo, Sung Woo Park, Heung Young Oh, Jin Bae Kim, Il Hyun Baek, Myung Seok Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2005;29(4):358-366. Published online July 1, 2005
- 1,365 View
- 27 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
A high prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease(GERD) has been reported in diabetic patient. However, the exact mechanisms of GERD in diabetic patient have not been described. In several studies, diabetic neuropathy and dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system have been suggested as risk factors of GERD. However, there have been no studies on the exact prevalence or risk factors of GERD in Korean diabetic patients. Therefore, the prevalence of GERD in Korean diabetics patients was examined, and the risk factors for GERD, the differences in symptoms between GERD and non-GERD patients, and the degree of symptom relief after treatment were also analyzed. METHODS: A total of 310 diabetic patients, who underwent an upper gastroendoscopy due to diverse gastrointestinal symptoms, between April 2001 and November 2003, were enrolled. The diagnostic criteria or GERD included the upper gastroendoscopic view, which was analyzed using the scale of 'The Los Angeles Classification of Esophagus' from grades A to D. The prevalence and symptoms of GERD patients and the variable risk factors, such as blood glucose level, smoking and diabetic neuropathy, were examined. RESULTS: 1) There was an 18.4% prevalence of GERD in diabetic patients. 2) The clinical characteristics, including sex, age and serum lipid level, of the GERD group were not significantly different to those of the control group. However, the duration of smoking, the fasting and postprandial 2-hour serum glucose levels, and the diabetic neuropathy significantly affected GERD, 3) The main symptoms of the GERD group were dyspepsia(47.4%) and heart burn(26.3%). 4) The degree of subjective symptom relief in the GERD group after treatment with the proton pump inhibitor, pantoprazole(40mg), was remarkably lower than in the control group for approximately 1 month. CONCLUSION: In this study, the prevalence of GERD in diabetic patient was higher than that found in the general population which suggests that GERD in diabetic patient was due to a poorly controlled serum glucose level and diabetic neuropathy. The chief complaints pertaining to gastrointestinal symptoms in both study groups were non-specific. However, the recovery from symptoms in the GERD group was lower than the control group following drug therapy. The causes of the lower response rate in the GERD group will need to be examined in further studies.
- The Influence of Metabolic Syndrome on the Intima-Medial Thickness and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Type 2 Diabetes.
- Kwang Pyo Son, Young Je Chae, Tae Yu Lee, In Kyung Jeong, Mina Hur, Gu Young Jo, Young Lee, Seong Jin Lee, Chul Young Park, Ki Won Oh, Eon Kyung Hong, Hyun Kyu Kim, Jae Myoung Yu, Doo Man Kim, Sung Hee Lim, Moon Ki Choi, Hyung Jun Yoo, Sung Woo Park
- Korean Diabetes J. 2004;28(5):392-406. Published online October 1, 2004
- 1,280 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Metabolic syndrome (MS) is usually present in type 2 DM (T2DM), and it is associated with atherosclerosis. The aim of this study is to exam the influence of MS on the intima-medial thickness(IMT) and the cardiovascular risk factors for type 2 diabetic patients. SUBJECTS AND METHODS: A cross sectional study was performed on 82 patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) and 84 healthy controls. MS was defined according to the NCEP-ATP III criteria. Those subjects with any history of cerebro vascular accident, ischemic heart disease or acute inflammation were excluded. The cardiovascular risk factors (hsCRP, lipid profile, homocysteine, and uric acid), the status of glucose metabolism (HbA1c, fasting glucose, insulin, and HOMA-IR), the diabetic microvascular complications and the IMT at both common carotid arteries were measured. RESULTS: 1) For patients with T2DM, the levels of waist circumference, blood pressure, TG (1.7+/-1.4 vs 2.2+/-1.4 mmol/L), HDL-C (1.5+/-0.4 vs. 1.3+/-0.3 mmol/L), LDL-C (2.7+/-0.7 vs 3.1+/-0.9 mmol/L), TC/HDL-C (3.5 vs. 41), log of (hsCRP) (-0.11+/-0.4 vs 0.17+/-0.4), mean carotid IMT (0.63+/-0.12 vs. 0.74+/-0.12 mm) and max IMT (0.68+/-0.14 vs. 0.86+/-0.15 mm) were significantly different from the healthy control group. 2) The prevalence of MS in the T2DM groups was 64%. However, a decrease of the waist circumference, as measured by the modified Asian criteria, increased the crude prevalence of MS by up to 75%. 3) Diabetic patients with MS had a higher incidence of hypertension, a lower level of HDL-C, and higher levels of waist circumference, HOMA-IR, TG, and TC/HDL-C, a greater extent of microvasculopathy, an increased log (hsCRP), homocysteine, and carotid IMT than did diabetic patients without MS. 4) Among the component of MS, the presence of hypertriglyceridemia had an influence on the IMT mean and max. 5) The carotid IMT of patients with DM correlated with age, homocysteine, log (hsCRP), and uric acid on univariate analysis, and age and homocysteine we found to be independent risk factors of carotid IMT on multivariated analysis. CONCLUSION: Metabolic syndrome in subjects with glucose intolerance increases the risk of atherosclerosis.
- Effect of Glucose Concentrations on the Cell Proliferation and Expression of L-type Calcium Channel mRNA in Cultured Rat Aortic Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells.
- Young Jung Cho, Hyung Joon Yoo, Hong Woo Nam, Ji Young Suh, In Kyung Jeong, Sung Hee Ihm, Hyeon Kyu Kim, Cheol Young Park, Jae Myung Yoo, Doo Man Kim, Moon Gi Choi, Sung Woo Park
- Korean Diabetes J. 2003;27(3):253-259. Published online June 1, 2003
- 1,180 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation is one of the major pathogenic mechanisms for atherosclerosis. It is known that L-type calcium channels play a role in VSMC proliferation in diabetic rats. However, there have been no studies that show an association between the L-type calcium channels and the VSMC proliferation due to various glucose concentrations in the culture media. Therefore, the association between the voltage-dependent L-type calcium channels of the VSMCs, and the growth of vascular smooth muscle cells, was examined. METHODS: Rat aortic VSMCs were isolated from the aorta of Sprague-Dawley and OLETF rats, using an enzymic method. The VSMCs were cultured in various concentrations of glucose (5.5, 11.0, 16.6, 25, 30 and 40 mM). The VSMCs (1x10(4) cells in 24-well plates) were incubated in the presence of Bay K 8644 (10(-6)M), both with and without verapamil (10(-6)M), for 48 hours. The proliferation was then assessed by the MTT (methylthiazole tetrazolium) assay, and the expression of L-type calcium channel mRNA by RT-PCR. RESULTS: The vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation was significantly increased, in a dose-dependent manner, with glucose concentrations below 25 mM in both in a dose-dependent manner, with glucose concentrations below 25 mM in both kinds of rat. However, the increase in the VSMC proliferation of the OLETF rat was significantly higher than in the Sprague-Dawley rat. After the Bay K 8644 treatment, with the same glucose concentration, the VSMC proliferation and the expression of L-type calcium channel mRNA were significantly increased in both kinds of rat. After treatment with verapamil, the increased VSMC proliferation and expression of L-type calcium channel mRNA, due to the Bay K 8644, were suppressed to control levels in both kinds of rat. CONCLUSION: The results suggest that below certain concentrations of glucose, 25 mM, the L-type calcium channels may play a role in the VSMC proliferation of OLETF and Sprague-Dawley rats. The growth of the VSMCs in OLETF rats, due to various glucose concentrations (< 25 mM), was significantly higher than in the Sprague-Dawley rats.
- The Significance of Hyperglycemia Control in Acutely Ill or Hopitalized Patients.
- Doo Man Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2003;27(2):85-94. Published online April 1, 2003
- 762 View
- 16 Download
- Prevention of Diabetes Mellitus: Including Review of Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study and Diabetes Prevention Program.
- Doo Man Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2001;25(4):251-257. Published online August 1, 2001
- 782 View
- 18 Download
- The Relation of Diabetes Control to Stress Amounts Associated with Life Events in Diabetics.
- Jung Won Lim, Hyung Joon Yoo, Kyung Ae Choi, Sung Hee Lim, Yoo Sun Chung, Sung O Seo, Chul Su Choi, Hyun Kyu Kim, Jae Myung Yoo, Doo Man Kim, Moon Gi Choi, Sung Woo Park, Young Joong Cho
- Korean Diabetes J. 2001;25(3):240-249. Published online June 1, 2001
- 1,082 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The life events which diabetic patients experience has an influence on conduct and communication pattern that is essential to control diabetes. The psychosocial life events which patients experienced in recently, as well as in the past has an important meanings in the process of the plan, implementation and evaluation of diabetic control. However, the most researches on this issues are scanty. Thus, we evaluated the relation of diabetic control to stress amounts associated with the life event which diabetic patients experience for the past one year. METHODS: In this study, 81 diabetic patients admitted to H hospital from March, 1999 to February 2000 were examined in stress amounts associated with life events, blood sugar, HbA1C, duration, complication, family history, treatment to inspect the hypothesis that stress experiences for recent 1 year are related to diabetic control. The 'Life Psychosocial Event Scale' invented by Lee was used. To examine the hypothesis that diabetic control may be influenced by the amount of stress, we investigated the difference of the means between the two groups (upper 30% of patients vs. lower 30% of patients) by T-test. RESULTS: The mean age was 56.9+/-15.1 years and the mean duration of diabetes was 8.9+/-7 years. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) was 200.3+/-71.0 mg/dL, PP2 was 292.9+/-87.2 mg/dL, HbA1C was 10.5+/-2.6%, complication was 0.8+/-0.9. The age showed negative correlation with stress amounts. The other variables did not show significant correlation with stress amounts. Thus, our study indicated that the hypothesis that stress experiences for recent 1 year are related to diabetic control was rejected. However, considering the perception-phenomenological approach on stress, if we study the relationship between stress with diabetic control inclusively, it seems that we can recognize such relationship. CONCLUSION: To address relation between stress with diabetic control inclusively, we need to consider stress factors in diversified aspects more than only one. Therefore, we must investigate how do patients perceive and cope with stress inclusively, because the crisis of life is influenced on the stress coping skill of patients. The study on this issue must be continued to identified the key factors associated with stress in diabetes.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





